Detailed Notes
Understanding Upper Assam and Lower Assam – The Two Cultural and Geographical Divisions of Assam
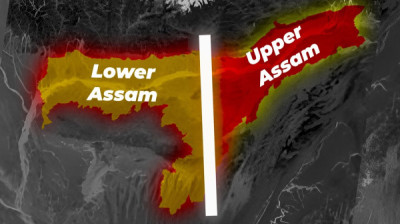
Upper Assam – The Land of Tea, Ahom Kings, and River Islands
Upper Assam covers the easternmost part of the state and includes districts such as Dibrugarh, Jorhat, Sivasagar, Golaghat, Tinsukia, Lakhimpur, Dhemaji, Majuli, and Charaideo. The region is historically significant as the center of the Ahom Kingdom, which ruled Assam for over six centuries and established a unique blend of Tai, Assamese, and Hindu cultures.
The Ahoms left a remarkable architectural legacy, visible in monuments like the Rang Ghar, Talatal Ghar, and the Sivasagar Tank. These structures reflect the engineering skill and cultural sophistication of that era. Culturally, Upper Assam preserves the purest form of Assamese language and traditions, and it remains a stronghold of the Vaishnavite movement initiated by Srimanta Sankardev. The Satras (monasteries) of Majuli, the world’s largest river island, continue to serve as centers of art, music, and spirituality.
Economically, Upper Assam is the industrial powerhouse of the state, often called the “Tea Capital of the World.” Districts like Dibrugarh and Jorhat host India’s oldest and largest tea plantations, while Digboi houses Asia’s first oil refinery. The region’s rich natural resources and biodiversity make it a significant contributor to Assam’s economy.
Lower Assam – The Spiritual and Cultural Heartland
Lower Assam lies in the western part of the state, encompassing districts such as Kamrup, Kamrup Metropolitan (Guwahati), Nalbari, Barpeta, Goalpara, Dhubri, Bongaigaon, and Baksa. Historically, this area formed part of the ancient Kamarupa Kingdom, one of India’s earliest Hindu dynasties.
The region is home to the world-famous Kamakhya Temple in Guwahati, one of the 51 Shakti Peethas, which attracts millions of pilgrims during the Ambubachi Mela. Lower Assam also displays a fusion of cultures due to its proximity to West Bengal and Bhutan, making it a melting pot of Assamese, Bengali, and Bodo linguistic and cultural influences.
Economically, Lower Assam is known for its fertile plains, trade activities, and tourism. Guwahati serves as the commercial hub and gateway to Northeast India, connecting the region to the rest of the country. Festivals like Bhogali Bihu, Ambubachi Mela, and Doul Utsav reflect the rich cultural vibrancy and inclusivity of this part of Assam.
Upper Assam vs. Lower Assam – Key Differences
While both regions share Assam’s spirit of unity, they differ in geography, lifestyle, and history. Upper Assam is characterized by lush tea estates, Ahom heritage, and Tai-Ahom rituals, whereas Lower Assam symbolizes spirituality, trade, and the ancient Kamarupa legacy. The dialects also vary — Upper Assam speaks standard Assamese, while Lower Assam carries linguistic shades influenced by neighboring cultures.
Together, Upper and Lower Assam represent the heart and soul of the state — a blend of history, nature, and humanity that continues to define Assam’s identity and pride.
Upper Assam vs. Lower Assam - Quick Info Table
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Topic | Upper Assam and Lower Assam |
| Region Type | Geographical and Cultural Division of Assam |
| Upper Assam Districts | Dibrugarh, Jorhat, Sivasagar, Golaghat, Tinsukia, Lakhimpur, Dhemaji, Majuli, and Charaideo |
| Lower Assam Districts | Kamrup, Kamrup Metropolitan (Guwahati), Nalbari, Barpeta, Goalpara, Dhubri, Bongaigaon, and Baksa |
| Major Rivers | Brahmaputra, Subansiri, and Dibang |
| Historic Kingdoms | Ahom Kingdom (Upper Assam), Kamarupa Kingdom (Lower Assam) |
| Cultural Identity | Tai-Ahom Heritage (Upper Assam), Kamakhya and Vaishnavite Traditions (Lower Assam) |
| Economic Highlights | Tea, Oil, and Natural Gas (Upper Assam); Trade, Tourism, and Agriculture (Lower Assam) |
| Major Cities | Dibrugarh, Jorhat (Upper Assam); Guwahati, Barpeta(Lower Assam) |
| Famous Attractions | Majuli Island, Sivasagar Monuments, Kamakhya Temple, Guwahati City, Ambubachi Mela |
FAQs on Upper Assam vs. Lower Assam
1. What is the difference between Upper Assam and Lower Assam?
Upper Assam lies in the east with Ahom heritage, while Lower Assam in the west is known for Kamakhya Temple and Kamarupa history.
2. Which districts are in Upper Assam?
Dibrugarh, Jorhat, Sivasagar, Golaghat, Tinsukia, Lakhimpur, Dhemaji, Majuli, and Charaideo.
3. Which districts are in Lower Assam?
Kamrup, Kamrup Metropolitan (Guwahati), Nalbari, Barpeta, Goalpara, Dhubri, Bongaigaon, and Baksa
4. What was the capital of the Ahom Kingdom in Upper Assam?
The Ahom capital was Charaideo, now an archaeological and cultural site.
5. What is Upper Assam famous for?
It is famous for its tea gardens, oil fields, and Ahom heritage sites.
6. What is Lower Assam famous for?
Lower Assam is known for Kamakhya Temple, Guwahati City, Ambubachi Mela city.
7. Which river flows through both Upper and Lower Assam?
The Brahmaputra River flows through both regions, connecting them geographically.
8. What are the major languages spoken in Upper and Lower Assam?
Upper Assam mainly speaks standard Assamese, while Lower Assam has Assamese, Bengali, and Bodo influences.
9. How is Guwahati important in Lower Assam?
Guwahati is the largest city and commercial hub of Lower Assam and the gateway to the Northeast.
10. Why is understanding Upper and Lower Assam important?
It helps appreciate Assam’s diverse history, geography, and cultural evolution across centuries.